Our brains communicate with electrical and baggy eyes eroticismchemical signaling, but scientists have discovered that light stimulation could hold potential keys to manipulating neuronal communication pathways that influence motor control, sensory perception, memory, neurochemical production and mood – or cellular virtual reality, as a report from the Journal of Cell Biology describes it.
With the roll out of the White House's $300 million BRAIN Initiative in 2013, interest in uncovering the secrets of the human brain has accelerated and now includes many government agencies, public/private partnerships and universities.
Dating back to at least 1971, optogenetic research has matured enough to gain the attention of organizations such as the NIH, DARPA and IARPA, who are exploring the role that light-sensitive cells could soon play in fields surrounding neurobiological, including physical and mental health, human-machine interfacing, and advancing artificial intelligence through reverse brain engineering.
Current optogenetic experiments rely on extracting "opsins" (light-sensitive proteins) from plants which can be introduced to mammals by methods including injection and infection via adenovirus.
Once delivered into an organism, opsins can be expressed in eye, brain or skin cells, allowing their light-sensitivity to be remotely activated or silenced with timed pulses of light in different color wavelengths across the light spectrum that can target multiple bodily systems and cause a variety of biological effects.
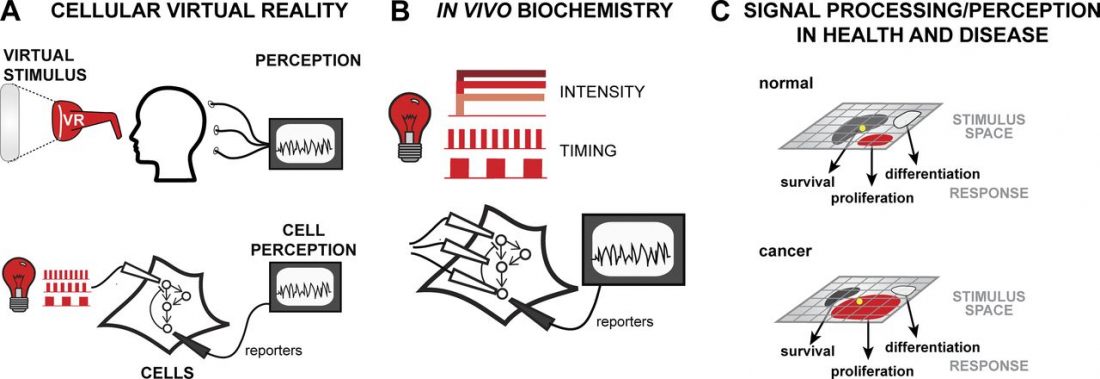
Researchers have suggested however that introducing opsins into an organism may not be a long-term requirement as methods are sought for using optogenetics on mammalian cells that respond naturally to light, such as those in the human retina.
As part of the BRAIN Initiative, scientists have been working on neuronal barcoding and completing a detailed online brain atlas for researchers. This is hoped to eventually provide a detailed circuit diagram of every neuron and synapse in the brain, which would allow various neuronal patterns to be identified so they can be triggered for the desired effect.
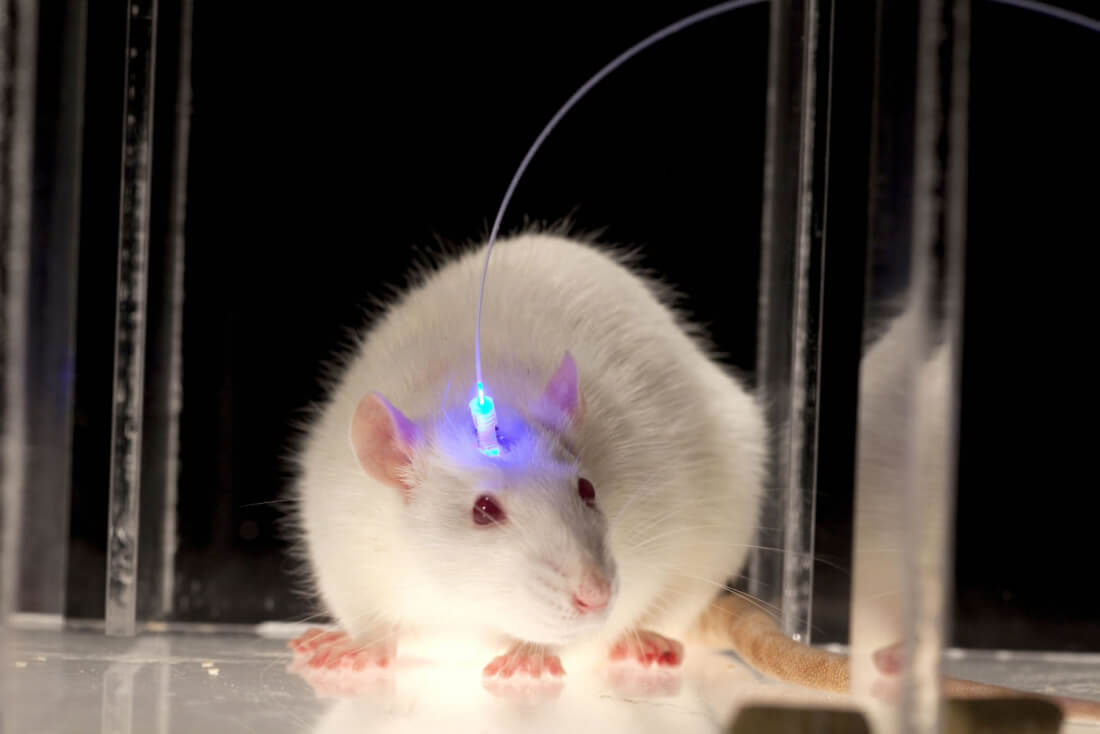
If targeted precisely enough with the appropriate light, it's thought that optogenetics could be used by manipulating neural circuits involved with pain, fear, reward, wakefulness and social behaviors. In one Yale study, for example, mice were infected with a virus which made their neurons sensitive to blue light. Scientists then used that light pathway to activate predatory behavior.
"...The researchers used a tiny optic fibre to shine a blue laser on the amygdala. This prompted the animals to tense their jaw and neck muscles... 'It's not just physiological, it's hunting, biting, releasing and eating. Those are motor sequences that require a lot of information...' [said an MIT neuroscientist]"
In 2015, optogenetics was combined with CRISPR to develop a set of photoactivatable tools that enable the editing of an organism's genome through the external use of light. Said tools can control the location, timing and reversibility of the genome editing process, whether that be activating, repressing or modifying a gene.
Optogenetics is also mentioned as an integral feature of the DARPA-funded Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program, a joint effort between six teams who are aiming to create an implantable neural interface over the next four years that is capable of high resolution brain-to-machine communication. Such advancements, for instance, could facilitate the development of mind-controlled prosthetics featuring touch sensation like the DARPA-backed 'Luke' arm (previously known as the 'Deka' arm).
In the past, DARPA has looked to optogenetic memory manipulation techniques for treating veterans with traumatic brain injury and/or PTSD through memory restoration or deletion.
More recently, during a November 2017 mental health conference with 30,000 attendees in Washington D.C., optogenetics was noted for the impact it's having on the ability to study the brain. According NPR science correspondent Jon Hamilton, the technology has allowed aspects of human mental health disorders to be reproduced in animals, aiding the mapping of neuronal circuits involved with issues such as depression.
Companies interested in the application of optogenetic technologies have begun emerging over the last decade, particularly since the FDA approved the technology in 2015 for use in treating an eye disorder known as "retinitis pigmentosa."
The approval prompted a clinical trial and optogenetic developments have since been used to restore partial vision in patients who were described as being "profoundly blind." Chronic pain management, epilepsy and Parkinson's are among many health issues that researchers are experimenting with addressing through optogenetics.
The technology is also contributing to other areas of research such as "sonogenetics," which uses low-pressure ultrasound to activate ultrasonically sensitized neurons. This is another area of interest for DARPA, which has funded Columbia University's endeavor to stimulate neurons using ultrasound and believes it could eventually lead to a magnetic version of the technology called "magnetogenetics."
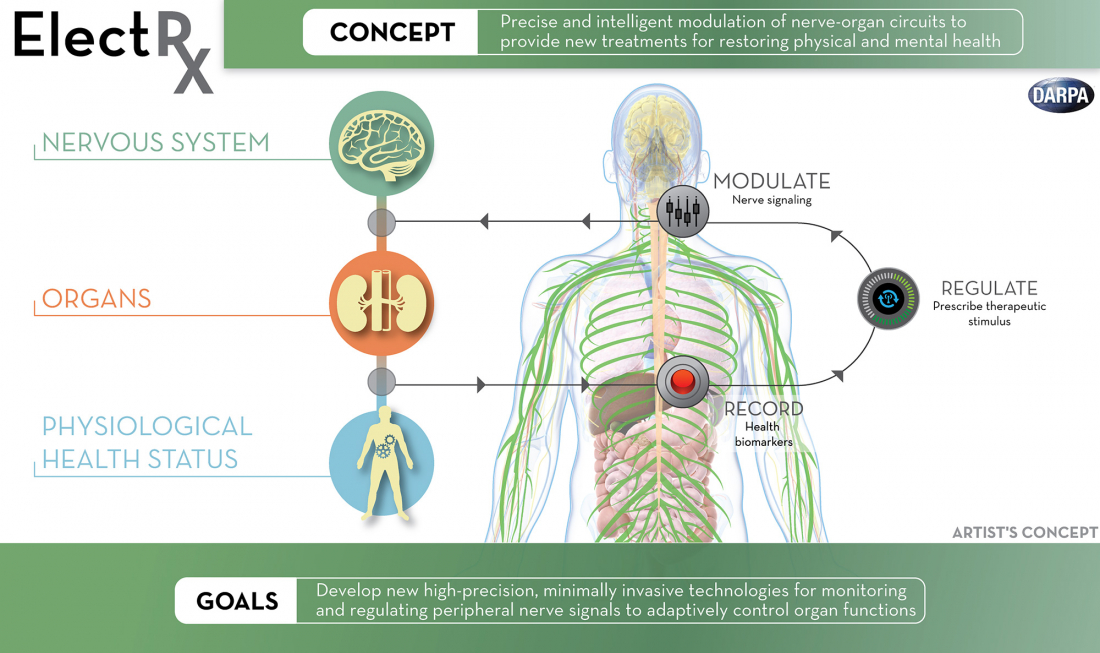
To investigate the therapeutic use of optogenetics, acoustics and electromagnetic fields, DARPA launched the ElectRX (Electrical Prescription) program in 2015, which is capable of stimulating, modulating and monitoring the body's peripheral nervous system. The research agency is also exploring how artificial intelligence could be used in closed-loop brain implants, such as the ability to detect patterns associated with mood disorders.
With enough progress, it's believed that optogenetics and its surrounding bodies of research may open the door to real-time brain mapping and biofeedback technologies, which could be used to treat all manner of ailments on the fly through closed-loop neuromodulation signals coming to and from an implanted device, ultimately eliminating the need for pharmaceuticals.
 Dallas Mavericks vs. Boston Celtics 2025 livestream: Watch NBA online
Dallas Mavericks vs. Boston Celtics 2025 livestream: Watch NBA online
 PewDiePie's new milestone proves his T
PewDiePie's new milestone proves his T
 Facebook 'Safety Check' activated amidst violent Charlotte protests
Facebook 'Safety Check' activated amidst violent Charlotte protests
 'Glass' is a disappointing sequel to 'Unbreakable' and 'Split'
'Glass' is a disappointing sequel to 'Unbreakable' and 'Split'
 Obama photographer Pete Souza on Trump: 'We failed our children'
Obama photographer Pete Souza on Trump: 'We failed our children'
 Hillary Clinton's new ad highlights Trump's misogynistic moments
Hillary Clinton's new ad highlights Trump's misogynistic moments
 'Harry Potter' fans, rejoice: You can now discover your true Patronus
'Harry Potter' fans, rejoice: You can now discover your true Patronus
 'Brooklyn Nine
'Brooklyn Nine
 NYT Connections hints and answers for February 5: Tips to solve 'Connections' #605.
NYT Connections hints and answers for February 5: Tips to solve 'Connections' #605.
 'Black Mirror' creator has a savage response to 'Bandersnatch' haters
'Black Mirror' creator has a savage response to 'Bandersnatch' haters
 Great white shark leaps into tiny boat, fisherman treats it like NBD
Great white shark leaps into tiny boat, fisherman treats it like NBD
 LG's extravagant 'Massive Curve of Nature' is the most mesmerizing thing at CES 2019
LG's extravagant 'Massive Curve of Nature' is the most mesmerizing thing at CES 2019
 Guy's plan to help homeless with McDonald's Monopoly goes viral
Guy's plan to help homeless with McDonald's Monopoly goes viral
 Lady Gaga apologizes for collaborating with R. Kelly, pulls duet from streaming
Lady Gaga apologizes for collaborating with R. Kelly, pulls duet from streaming
 The White House might have inflated Trump's golf record, because this is how we live now
The White House might have inflated Trump's golf record, because this is how we live now
 Hillary Clinton's new ad highlights Trump's misogynistic moments
Hillary Clinton's new ad highlights Trump's misogynistic moments
 Guy's plan to help homeless with McDonald's Monopoly goes viral
Guy's plan to help homeless with McDonald's Monopoly goes viral
 Facebook 'Safety Check' activated amidst violent Charlotte protests
Facebook 'Safety Check' activated amidst violent Charlotte protests
 We'll always, er, sorta, have the Paris Climate Agreement
We'll always, er, sorta, have the Paris Climate Agreement
 Amazon's Jeff Bezos announces he and wife MacKenzie are getting a divorce
Amazon's Jeff Bezos announces he and wife MacKenzie are getting a divorce
Teetering Canaries by Judith SchalanskyTikTok CEO Shou Zi Chew is Singaporean, not Chinese. Somebody please convince Senator Tom Cotton.YouTuber creates 20Against Remembrance: On Louise Glück by Elisa GonzalezBest smart glasses deal: The Amazon Echo Frames are under $210 at AmazonThe Sphere by Elena Saavedra BuckleyBeginning with Color: An Interview with Etel Adnan by Laure AdlerA Fall Dispatch from the Review’s Poetry Editor by Srikanth ReddyPaul Bowles in Tangier by Frederic TutenGoogle releases sneak peek of its Super Bowl commercialVision Pro apps are now visible on Apple's App Store websiteThe Paris Review’s Favorite Books of 2023 by The Paris ReviewSyllabus: Unexpected Dramaturgy by Lynn NottageHulu and ESPN+ will crack down on password sharing, following Disney+Syllabus: Unexpected Dramaturgy by Lynn NottageSpaceX sticks daytime rocket landing back on Earth after launch to spaceAgainst Remembrance: On Louise Glück by Elisa Gonzalez’88 Toyota Celica by Sam AxelrodHow to edit photosTwo Strip Clubs, Paris and New Hampshire by Lisa Carver Smut by Sadie Stein The Mail Room by Sam Sweet William Weaver, 1923–2013 by Sadie Stein “The House We Live In”: Elizabeth Bishop on the Big Screen by Magdalena Edwards Let the Memory Live Again, and Other News by Sadie Stein Cinematic Librarians, and Other News by Sadie Stein Give the Gift of The Paris Review! by The Paris Review It Involves Breaking Stuff by Sadie Stein Teeth Marks: Three Early Poems by Albert Cossery by Anna Della Subin It Was Too Strong: An Interview with Todd Hido RIP Charlotte Zolotow, and Other News by Sadie Stein See You There: St. Mark’s Fundraiser by Sadie Stein Conversing with Brodsky, and Other News by Sadie Stein The News You Have Been Waiting For by Sadie Stein “I Would Like to Write a Beautiful Prayer” by Katherine Faw Morris Instead of the Cross, the Albatross by Sadie Stein Here Be Dragons by Sadie Stein On Not Thinking Like a Writer, and Other News by Sadie Stein Fasten Your Seatbelts, It’s Our Winter Issue by Sadie Stein The Great Columbia Book Slide of 1934 by Sadie Stein
3.0617s , 10218.7109375 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【baggy eyes eroticism】,Wisdom Convergence Information Network